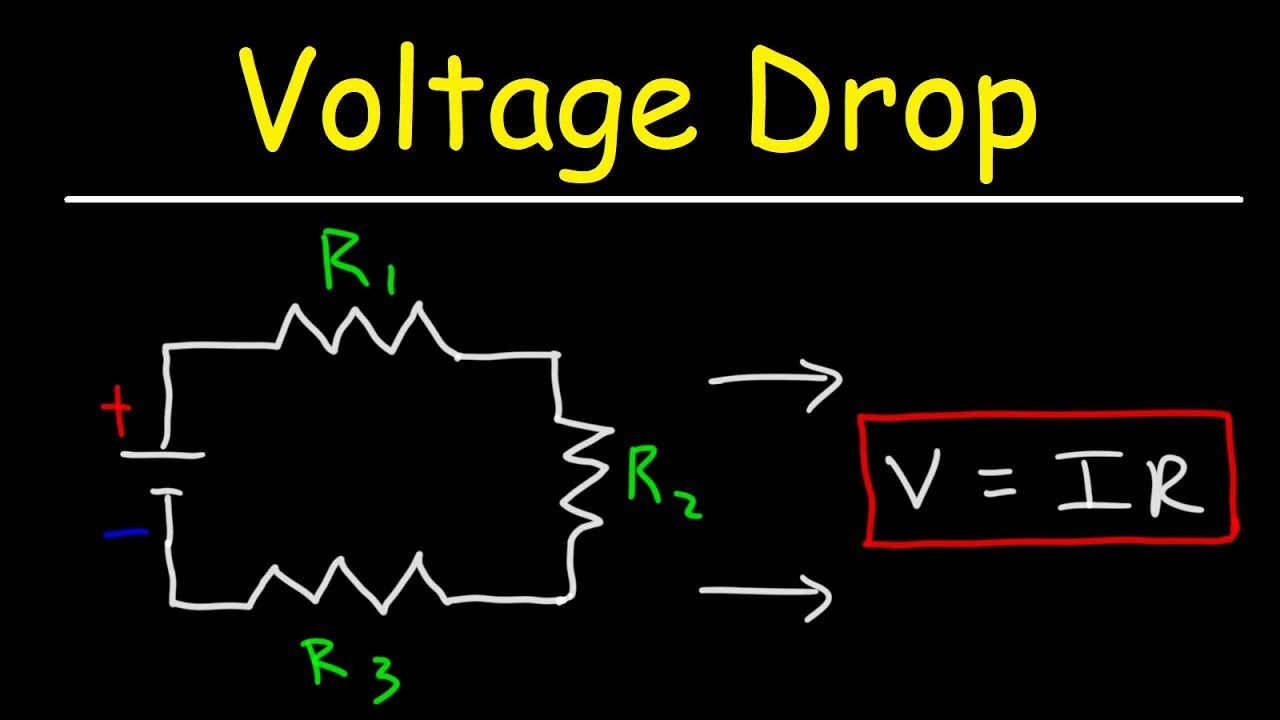
Calculating voltage drop across a resistor in parallel
SeriesParallel Resistor Calculator - SeriesParallel Resistor Calculator is a combination of Series circuit calculator and Resistor Parallel Calculator. Signals and Amplifiers 4 CHAPTER 2 Semiconductors 124 CHAPTER 4 MOS Field-Effect Transistors MOSFETs 230 Bipolar Junction Transistors BJTs 350 Devices and Basic Circuits.

How To Calculate Voltage Drop Across Resistor Detail Explaination Sm Tech
For condition 1 you dont want the resistors value too low.
. The voltage across this resistor is negative since were moving from the high potential side to the low potential side and is represented by -20I. Now that we know the amount of current through each resistor we can use Ohms Law to determine the voltage drop across each one applying Ohms Law in its proper context. When talking about the voltage drop across a resistor we are referring to the voltage across a resistor or the voltage once the current flow has gone through a resistor.
The potential difference across each resistor is same as the resistors are connected in parallel and the voltage across these resistors are the same. Conversely since the voltage drop across the 10 resistor is least it would be the dimmest bulb. We do the same thing for the other two resistors.
The voltage drop across each resistor The current through each resistor. Find the Equivalent Voltage Vs. See our Inductance Calculator.
Lets say a circuit with two parallel resistors is powered by a 6 volt battery. Since the voltage drop across the 30 resistor is greatest it would be the brightest bulb. 1 μH 0000001 10⁶ H.
However the voltage drop across all of the resistors in a parallel resistive network IS the same. As the first switch SW1 is closed the voltage across resistor R1 will increase to full battery voltage while the. If you know the voltage across the whole circuit the answer is surprisingly easy.
V P 1 R 1. We can calculate the amount of allowable ripple by the formula below. This much quicker product-over-sum method of calculating two resistor in parallel either having equal or unequal values is given as.
Ω is the SI unit of electrical resistance named after. The value of the pull-up resistor controls the voltage on the input pin. Use the total voltage to find the voltage across each resistor.
The total resistance of. In this configuration the voltage drop across each resistor is the same. The overall voltage is 1414 V so the resulting power equals 20 W.
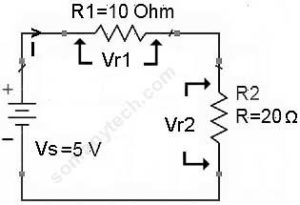
The total resistance R total in a series circuit is simply the sum of the individual resistances so. 1 pH 0000000000001 10¹² H. Using Ohms law calculate the voltage drop across each resistor.
We start by calculating the total resistance of Parallel Circuit 1. Calculate the power dissipated by the second resistor R 2 P 2 V 2 R 2. Find the voltage V across resistor R 1 of power rating P 1 using the formula.
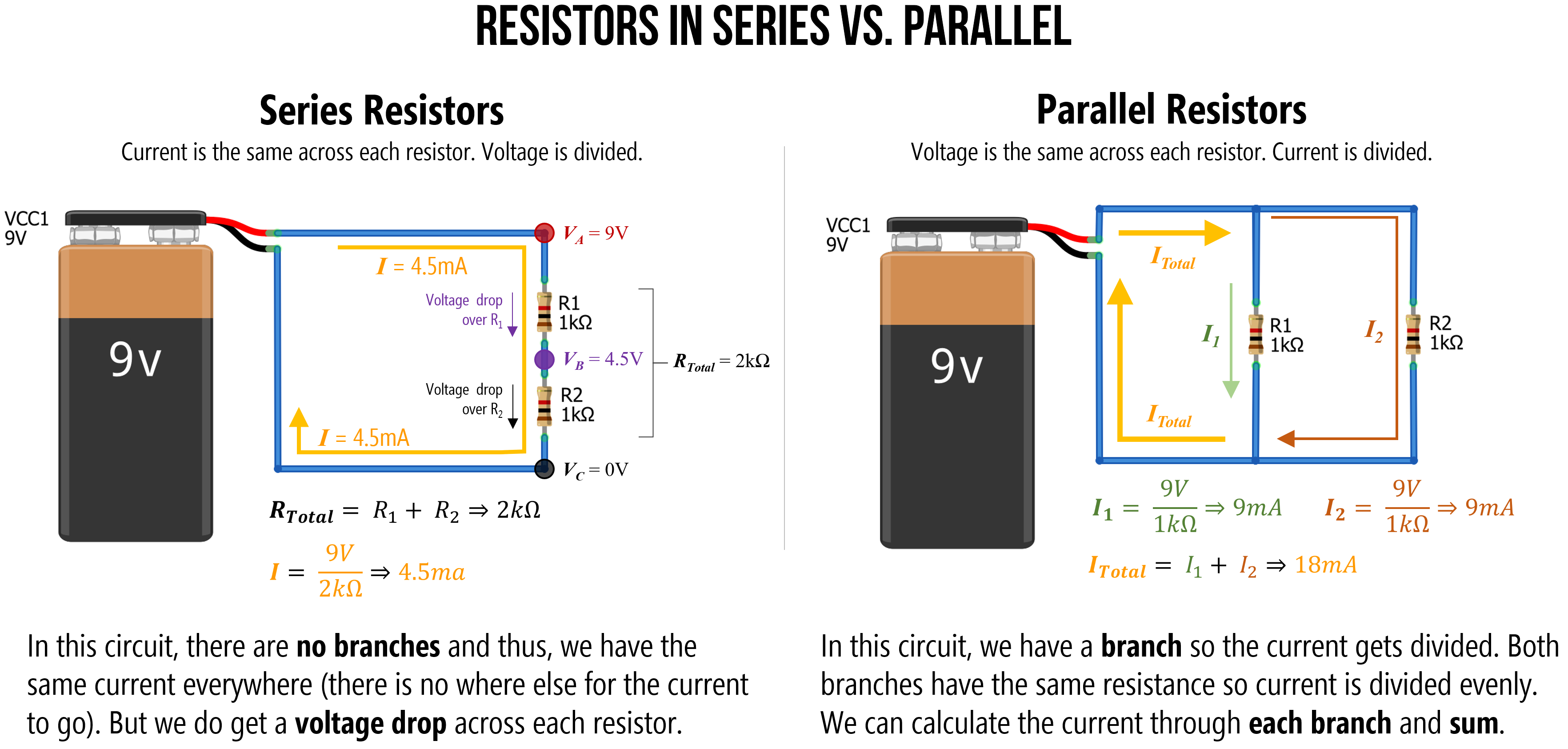
As we know a resistor is a passive electrical element that provides electrical resistance to the flow of current. In the image above you will see two circuits. Calculating Resistance for a Series Circuit.
Since the voltage drop across all the resistors combined must be the same as the voltage drop across the cell in a series circuit we can find V_3 using. The voltage drop is also known as IR drop. Thus according to ohms law it will create a voltage drop when the current passes.
Resistors in Parallel Example No2. In the circuit diagram given below the current flowing across 5 ohm resistor is 1 amp. This voltage divider equation can be used for any number of series resistances connected together because of the proportional relationship between each resistance R and its corresponding voltage drop VNote however that this equation is given.
Notice the voltage drops across each resistor and how the sum of the voltage drops 15 5 25 is equal to the battery supply voltage. Given I 1 amp. Because 15 divided by 6 is 25 the current would be 25 amperes.
The distinction between series and parallel circuits is highlighted by calculating the total resistance from several resistors. The current now has several paths and can vary depending on which resistor you use. V AB Then the Thevenins Equivalent circuit is shown below with the 40Ω resistor connected.
You generally want a large resistor value 10kΩ but you dont want it too large as to conflict with condition 2. The first circuit with only one resistor and the second circuit with two resistors. Find the current flowing through the other two resistors.
Ohms law states that the voltage across a resistor is proportional to the current passing through it where the constant of proportionality is the resistance For example if a 300-ohm resistor is attached across the terminals of a 12-volt battery then a current of 12 300 004 amperes flows through that resistorThe ohm symbol. V VpeakCap- Vmin. The voltage across the left resistor is 6 volts and the.
V Rx is the voltage drop across the resistor R X is the value of the resistor and R T is the total resistance of the series network. For the peak voltage across the transformer primary to be 17V12sqrt2 and the total drop across the diodes to be 207V 14V the peak voltage across the capacitor is about 15V approx. So the voltage drop across the 20Ω resistor can be calculated as.
We now need to reconnect the two voltages back into the circuit and as V S V AB the current flowing around the loop is calculated as. Each parallel wire has the same voltage as the entire circuit. The equation for calculating total resistance in a parallel circuit for any number of parallel resistances is sometimes written like this.
The lower the resistance the more power will be used when the button is hit. In a parallel circuit there is more than one loop or. 1 mH 0001 H.
When a 15 Volt battery is connected in parallel with a 6-ohm and 2-ohm resistor the current flowing through the 6-ohm resistor is equal to the voltage across the 6-ohm resistorthat is 15 Volts divided by the resistors value of 6 ohms. In this case the current through each resistor is the same so V determines the brightness. Beginalign V V_1 V_2 V_3 V_3 V - V_1 - V_2 18 - 2 - 6 V_3 text10text V endalign.
In a parallel connection of resistors the voltage across each resistor is the same. Inductance characterizes the ability of an electrical conductor to convert changes in electric current into changes in electrical potential in both this conductor self-inductance and in any nearby conductors mutual inductance. 1 nH 0000000001 10⁹ H.
R 5 ohm. The voltage drop across a resistor is nothing but simply a value of voltage across the resistor. Understanding Voltage Drop Across a Resistor.
How To Calculate The Voltage Drop Across A Resistor Electronics Youtube

Determine The Voltage Drop Across The Resistor R 1 In The Circuit Given Below With E 65v R Youtube

How To Calculate Voltage Drop Across Resistor Detail Explaination Sm Tech
How To Calculate Voltage Drop Across Resistor Detail Explaination Sm Tech

How To Calculate Voltage Across A Resistor With Pictures
L4 Series And Parallel Resistors Physical Computing

How To Calculate Voltage Across A Resistor With Pictures

Circuit Analysis Solving Current And Voltage For Every Resistor Youtube

How To Calculate Voltage Across A Resistor With Pictures

Current Voltage Drop Across A Single Resistor And Across Two Resistors Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange

Resistors In Parallel Parallel Connected Resistors

Series Parallel Circuits How To Find Voltages Of Resistors And Currents Of Resistors Youtube

Resistors In Series Series Connected Resistors

Resistors In Parallel Parallel Connected Resistors
In A Circuit With A Series And Parallel Connection Of Resistors How Should I Calculate For A Voltage Drop Quora

How To Calculate Voltage Across A Resistor With Pictures
6 2 Resistors In Series And Parallel Introduction To Electricity Magnetism And Circuits